Environmental Chemistry at UMCES
Environmental chemistry is the branch of chemistry that studies chemical compounds’ movement within air, water and soil, affecting their ecosystems. Environmental chemists also attempt to comprehend the health hazards caused by chemicals present in our environment and how these can be reduced.
The Environmental Science Program (ESC) at UMCES strives to educate students about human-nature interactions. The curriculum incorporates studies of coastal and freshwater ecosystems in order to give a comprehensive view of how best to address current and emerging environmental problems.
By visiting mywikistory and ecommerc you can get more knowledge about multiple topics.
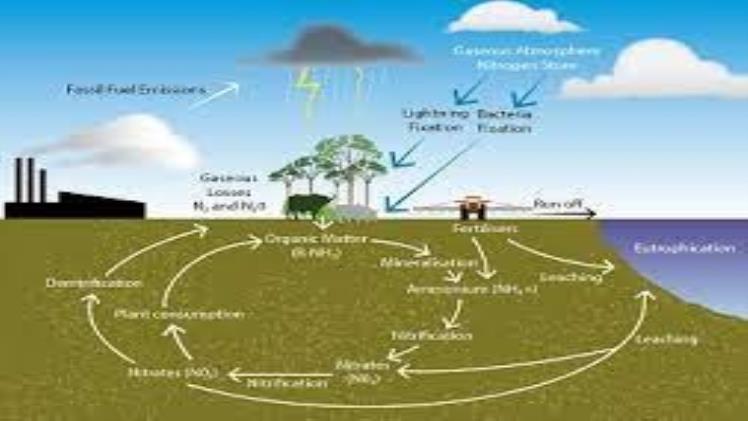
Researchers in the ESC study processes that shape our environment, such as sediment movement, nutrient cycling and seawater/lakebed chemistry. They employ cutting-edge instrumentation to measure and model water quality, sedimentation rates and pollutants’ effects on marine and estuarine environments.
Environmental chemists specialize in research areas such as geochemistry, aquatic chemistry and toxicology. Furthermore, they assess the environmental effects of industrial waste disposal.
Topics for Environmental Chemist Research Projects
Environmental chemist research projects typically address pollution-related topics. These may include:
Environmental Chemists Utilize Chemistry to Control Acid Rain and Air Pollution
Since 1960 when the Environmental Protection Agency began regulating pollutants and informing people about their potential health hazards, environmental chemists have been at the forefront of pollution control. Today, this field continues to evolve with new technologies being developed for this purpose.
Environmental chemists also study climate change. They aim to understand how human activities have caused changes in our climate and identify ways we can mitigate their effects.
Environmental chemists are always searching for solutions that will benefit our planet, from improving air quality to safeguarding food supplies and oceans. No matter their focus, environmental chemists strive to find sustainable solutions.
These solutions can range from developing alternative fuels to improving waste materials management and landfills. Furthermore, they may be utilized to identify potential pollutants or invasive species in oceans or on land.
Environmental chemists frequently conduct laboratory research and experimentation. They often collaborate with experts from other fields, such as hydrogeology or biology.
Environmental chemistry’s primary purpose is to keep Earth clean and healthy for people to live in. This is accomplished by identifying and preventing toxic chemical releases into either the atmosphere or soil.
Pollutants exist in many forms, from industrial sources, agriculture and mining.
These chemicals can be hazardous to our health and the environment, leading to cancer, kidney, or liver damage in humans. Furthermore, some of them cause birth defects and reproductive issues in animals.