Types of Wind Turbines
Wind turbines are machines that convert the kinetic energy of wind into electricity. They play a significant role in renewable energy infrastructure, especially onshore and offshore wind power projects.
Wind power is the most efficient way to generate electricity, and over the past five years its global weighted average levelised cost of electricity (LCOE) has decreased due to lower costs associated with installation and advances in technology.
Wind turbines consist of three primary components: the rotor, held high above the ground by a tower; the generator; and nacelle. These parts are usually made out of steel, aluminium or cast iron. The rotor is connected to the generator via an input shaft, producing energy which is then transmitted back to an electrical grid. Please click for more info: Jio Rockers Kannada
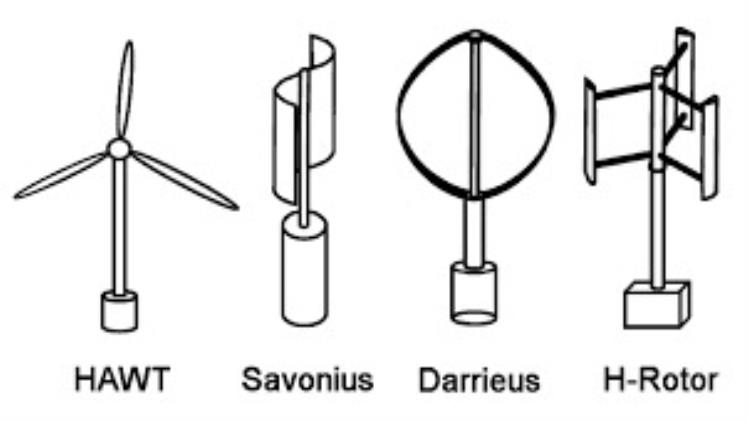
Horizontal-axis turbines are the most commonly used wind turbine type. These three-bladed models with an elongated shaft resemble propellers on airplanes.
visit for multiple topics news: Apkmirror4u and fmmagazines
Vertical-axis turbines, also referred to as eggbeaters or Darrieus turbines, have blades attached at both the top and bottom of a vertical rotor. Although these have been around for centuries, they no longer find widespread application due to their inefficiency compared with horizontal-axis wind turbines.
Some of the most commonly used wind turbines are a horizontal-axis wind turbine (HAWT) and vertical-axis wind turbine (VAWT). These types are frequently seen in media sources and used for various purposes.
Wind turbines come in a range of sizes, efficiency levels and construction materials; however they all share one thing in common: their purpose: to convert wind energy into electrical energy.
Larger wind farms require larger turbines in order to generate enough electricity. These bigger machines may be an advantageous investment, as they help boost land value and offer employment opportunities within the supply chain.
When designing a wind farm, it’s essential to factor in noise levels. This is particularly pertinent in areas where residents already live close by the farm. Studies have suggested that noise levels near wind farms may have an impact on people’s health, including their ability to sleep and overall sense of well-being.
Living close to a wind farm can have an adverse effect on quality of life, but there are ways to mitigate this. Sitting turbines carefully within sensitive landscapes as well as screening from features like trees and hills can help reduce noise pollution from nearby wind farms.
There is evidence to suggest noise levels near wind farms may affect people’s health, including their sensitivity to sound and ability to sleep. There’s also proof suggesting noise can impact people’s overall sense of wellbeing – including their capacity for restful nights and overall feelings of contentment.



